Create Processor and Workload¶
The next step is very similar to step 3 where you created a VPC with Policy Orchestrator Nodes, however, now you must create the Processor and Workload nodes within a new VPC. Be aware that some of the commands may appear very similar to prior commands, however they do have different consequences.
Create VPC¶
To create a new VPC for application deployment, with the cloud and region names– in this
example azr and westus-as an argument:
(myfab2) bwctl> create vpc azr westus
You should see output similar to:
[2019-09-25 17:51:51.688] Creating VPC: azr2-vpc-myfab2...
...
[2019-09-25 17:52:50.803] VPCs ['azr2-vpc-myfab2'] created successfully
Create Processor Node¶
Next, to create a processor, run the command with the target VPC name as an argument:
(myfab2) bwctl> create processor azr2-vpc-myfab2
You should see output similar to:
[2019-09-25 17:53:22.613] Creating new processor 'azr2-p01-myfab2'...
...
[2019-09-25 17:57:27.735] ['azr2-p01-myfab2'] created successfully
[2019-09-25 17:57:27.763] Generating SSH config...
To configure the processor, you will use the FQDN of orchestrator southbound interface (SBI).
The FQDN of orchestrator SBI has been auto-generated on the prior step and in this example has the structure as follows:
controller-myfab2.myorg2.poc.bayware.io
Note
The FQDN of orchestrator SBI is always defined in the following manner: controller-<fabric>.<company>.<DNS hosted zone>
To configure the processor, run the command with the FQDN of orchestrator
SBI – in this example controller-myfab2.myorg2.poc.bayware.io as an argument:
(myfab2) bwctl> configure processor azr2-p01-myfab2 --orchestrator-fqdn controller-myfab2.mayorg2.poc.bayware.io
You should see output similar to:
[2019-09-25 17:58:58.573] Generate ansible inventory...
...
[2019-09-25 18:00:18.506] Processors ['azr2-p01-myfab2'] configured successfully
To start the processor, run the command:
(myfab2) bwctl> start processor azr2-p01-myfab2
You should see output similar to:
[2019-09-25 18:00:44.719] Processors to be started: ['azr2-p01-myfab2']
...
[2019-09-25 18:00:47.537] Processors ['azr2-p01-myfab2'] started successfully
Create Workload Node¶
Now create a new workload in the current VPC, run the command:
(myfab2) bwctl> create workload azr2-vpc-myfab2
You should see output similar to:
[2019-09-25 18:03:26.462] Creating new workload 'azr2-w01-myfab2'...
...
[2019-09-25 18:06:24.269] ['azr2-w01-myfab2'] created successfully
[2019-09-25 18:06:24.297] Generating SSH config...
To configure the workload, run the command with the FQDN of orchestrator SBI – in this example controller-myfab2.myorg2.poc.bayware.io as an argument:
(myfab2) bwctl> configure workload azr2-w01-myfab2 --orchestrator-fqdn controller-myfab2.myorg2.poc.bayware.io
You should see output similar to:
[2019-09-25 18:07:17.658] Generate ansible inventory...
...
[2019-09-25 18:08:25.858] Workloads ['azr2-w01-myfab2'] configured successfully
To start the workload, run the command:
(myfab2) bwctl> start workload azr2-w01-myfab2
You should see output similar to:
[2019-09-25 18:09:18.375] Workloads to be started: ['azr2-w01-myfab2']
...
[2019-09-25 18:09:21.495] Workloads ['azr2-w01-myfab2'] started successfully
Check Resource Graph¶
To verify that both the processor and workload nodes have joined the service interconnection fabric, go to orchestrator and click on Resource Graph.
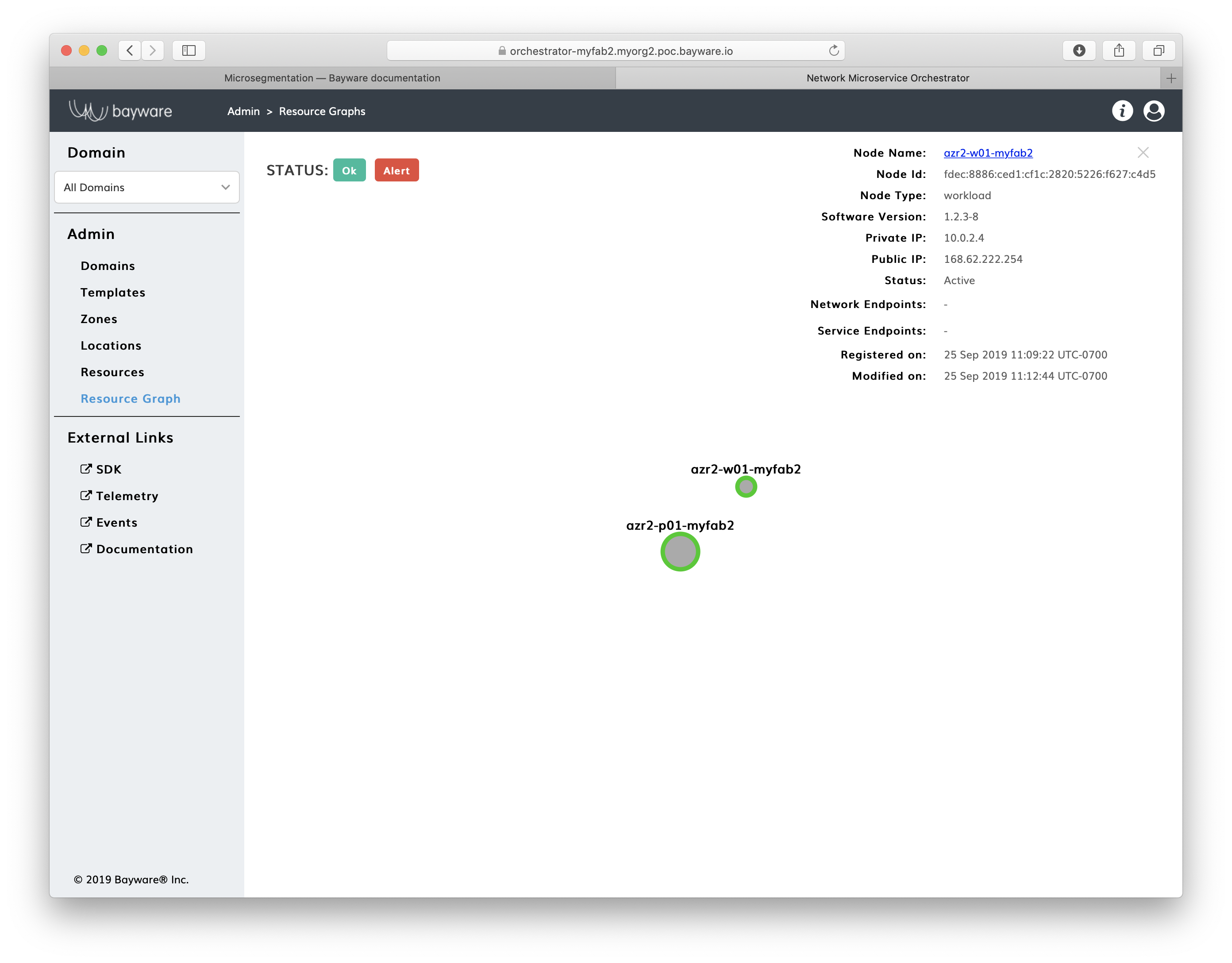
Fig. 11 Fig. Orchestrator Resource Graph Page